About Our Service Reports
Learn more about your Waterloo Bio-Filter Service Report. Hover your mouse pointer over the various fields in the sample report for a detailed explanation of each section.
For question regarding the details of your most recent report please contact our service department at [email protected]
Page One Definitions
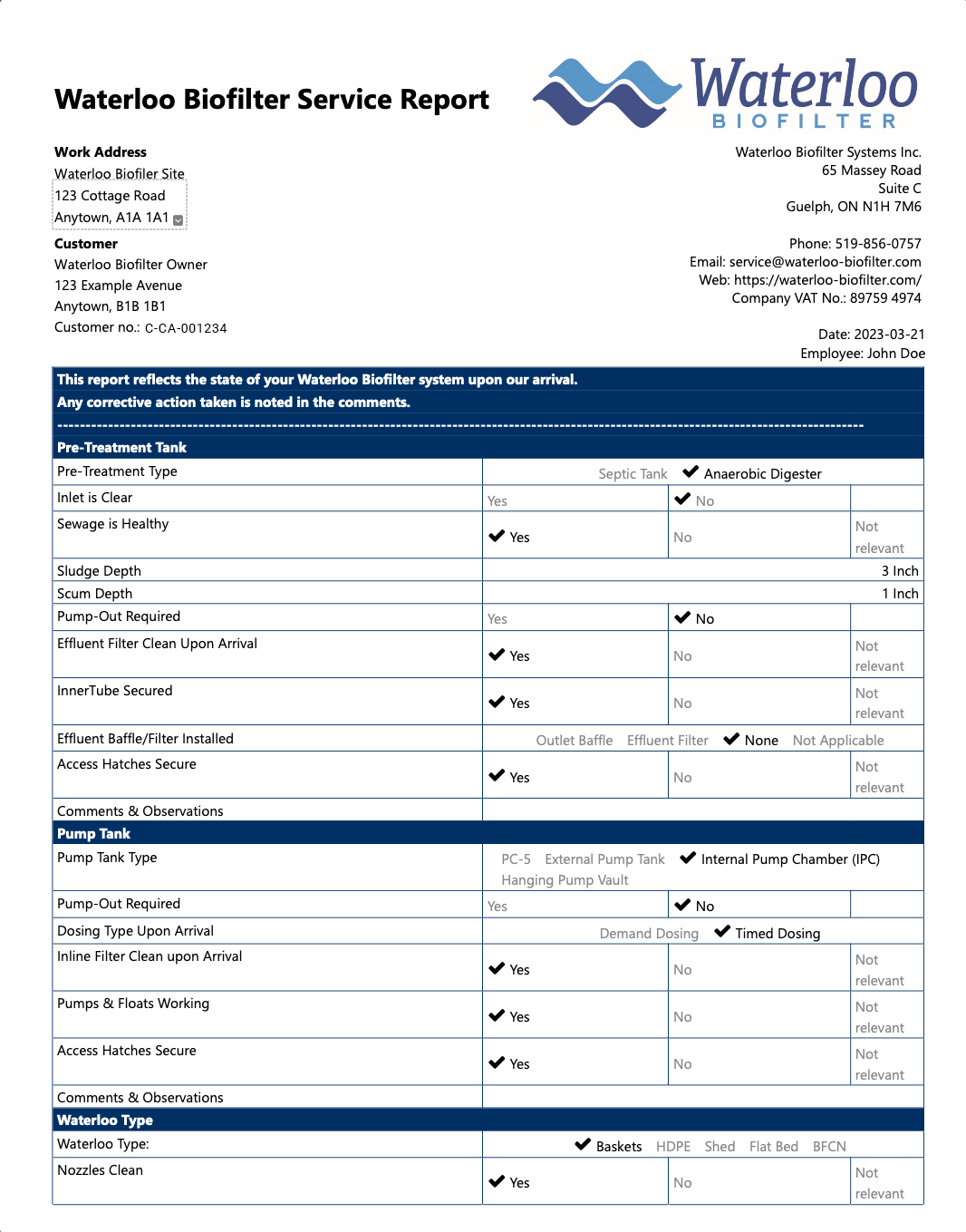
Work Address
The physical address of the property with the Waterloo Biofilter wastewater treatment system.
Date
This is the date of the service visit.
Customer
The customer name and billing address. If any of your information has recently changed, please contact our office so we can update our records.
Employee
This is the name of the service technician who performed the service. When more than one technician attends your site, only one technician will fill out the form.
Pre-treatment Tank Section
This is the first step in the treatment system.
Pre-treatment Type
The technician will check off which style of pre-treatment system you have. A septic tank is a single walled tank that divides the solids from the liquids. Liquids are pumped further into the system for treatment. An anaerobic digester is similar to a traditional septic tank with a corrugated tube that runs along the entire perimeter of the septic tank. This tube allows for a longer retention time to break down solids.
Inlet Clear
The inlet is the opening where the plumbing from the house or building enters the septic unit. The technician looks for any thing blocking the opening, or for evidence of materials entering the septic system that should not be going down the drain.
Sewage is Healthy
Signs of healthy sewage can include the presence of fermentation bubbles which indicate active digestion is occurring. Technicians will also look for signs of material that should not be entering the septic system and may result in ineffective treatment, or pose potential problems to the system, such as non-flushable items (e.g. paper products, plastic, and other detrimental items). Systems that have been recently started up may not have had sufficient time or received sufficient volume of sewage into the tank to develop the necessary bacterial colonies for treatment. In those instances, the sewage is not expected to be healthy yet and it is not a concern; in this case the technician will select “no” and may reiterate that in a comment.
Sludge Depth
“Sludge” refers to the separated solids that accumulate on the bottom of the tank.
The sludge depth is a measurement of the solids at the bottom of the tank.
Scum Depth
“Scum” refers to fats, oils, and greases (FOG). Scum also contributes to what is referred to as the 'Bio-mat' floating at the top of the chamber. Scum forms the bottom of the mat and on top of the scum there may be a layer of mold, debris, bugs, etc.
The scum depth is a measurement of the layer of matter floating at the top of the chamber.
Pump-out Required
If the technician checks "yes," it means the combined level of sludge and scum have reached the level that recommends a pump out. Owners are responsible for contacting an independent pumping provider.
Effluent Filter Clean Upon Arrival
The effluent filter is what keeps solids and particulate over 1.6mm from entering the pump tank. The technician will remove the filter and note if it is clean or not; this also gives us an indication of what is going into the system and if best practices need to be reviewed. The technician will rinse the filter clean and re-install it.
InnerTube Secured
The InnerTube acts like the intestines of the digester; it encourages retention and this is where breakdown of solids occurs. The InnerTube should be secured to the side of the tank at the inlet.
Effluent Baffle/Filter Installed
The effluent baffle or effluent filter help to prevent scum from migrating to the pump tank.
Access Hatches Secured
The technician checks off whether the access hatches are secured in place when they depart.
Pre-treatment Comments & Observations
This is where the technician will add commentary to the points above such as their observations of the sewage (odour), if a pump out is required or strongly advised, if the innertube was airlocked or clogged; hazards in the work area, or anything else they want to make note of for future reference. The technician will also note any steps they took to resolve an issue such as an airlock or clog.
Common comments you may see are:
- Level was high in digester tube, poked holes to release airlock
- Evidence tank was flooded at some point
- Effluent filter had a moderate accumulation of slime
- Poor sewage health, likely caused by the amount of non-digested toilet paper in the sludge layer
- Tank is almost at 1/3 capacity; owner is advised that a pump out should be scheduled for this season
Pump Tank
The pump tank moves sewage to the treatment zone.
Pump-out Required
The technician will advise it the pump tank needs a pump-out. Sometimes both tanks will need a pump out at the same time and sometimes only one chamber will need a pump out. If one chamber needs a pump out it is advisable to have both chambers pumped out for convenience.
Dosing Type Upon Arrival
Demand Dosing: The pump turns on when the float raises and triggers the pump to engage. The pump will stay on until the level decreases and the float is no longer lifted. This means sewage will continue to move to the treatment zone in a steady stream. This system does not use a timer.
Timed Dosing: When a float is lifted a timer is engaged and controls the pump through cycles of off and on mode designed to gradually move the sewage to the treatment zone on a timed basis for better treatment.
Dosing Filter Clean Upon Arrival
The purpose of the inline filter is to prevent debris or material from plugging or breaking the spray nozzles. The technician will remove the filter and note if it is clean or not; this also gives us an indication of what is going into the system and if best practices need to be reviewed. The technician will clean the filter clean and re-install it.
Pumps & Floats Working
The technician will test the floats by manually raising them to ensure they are engaging and sending a signal to the panel to trigger the pump or timer. The technician will look for evidence the pump or timer is engaging. The technician will also test the amps that the pump is drawing as it works.
Pump Comments & Observations
This is where the technician will add commentary to the points above and notes any action or work completed.
Waterloo Type Section
The Waterloo type is the treatment configuration of your system.
Waterloo Type
Various Types of Waterloo
Baskets: The filtration media is contained in a wire basket and placed into the concrete tanks. This is where the majority of the treatment takes place.
HDPE: The filtration media is contained in a plastic tank. The tank is about two thirds media with the remaining third occupied by effluent which will be pumped to the disposal bed.
Shed: Similar in appearance to a garden shed, these free-standing sheds contain one or more baskets of filtration media.
Flat Bed: Recognizable by an above grade fixture covered in pine bark, the bulk of the treatment unit is located underground.
BFCN: A large sea or shipping container filled with treatment media. These are typically seen in large scale applications.
Nozzles Clean
(Applicable treatment units) spray nozzles are utilized to distribute the sewage effluent over the treatment media. The technicians remove the nozzles from the clip that attaches them to the manifold and cleans them to remove any debris.
Page Two Definitions
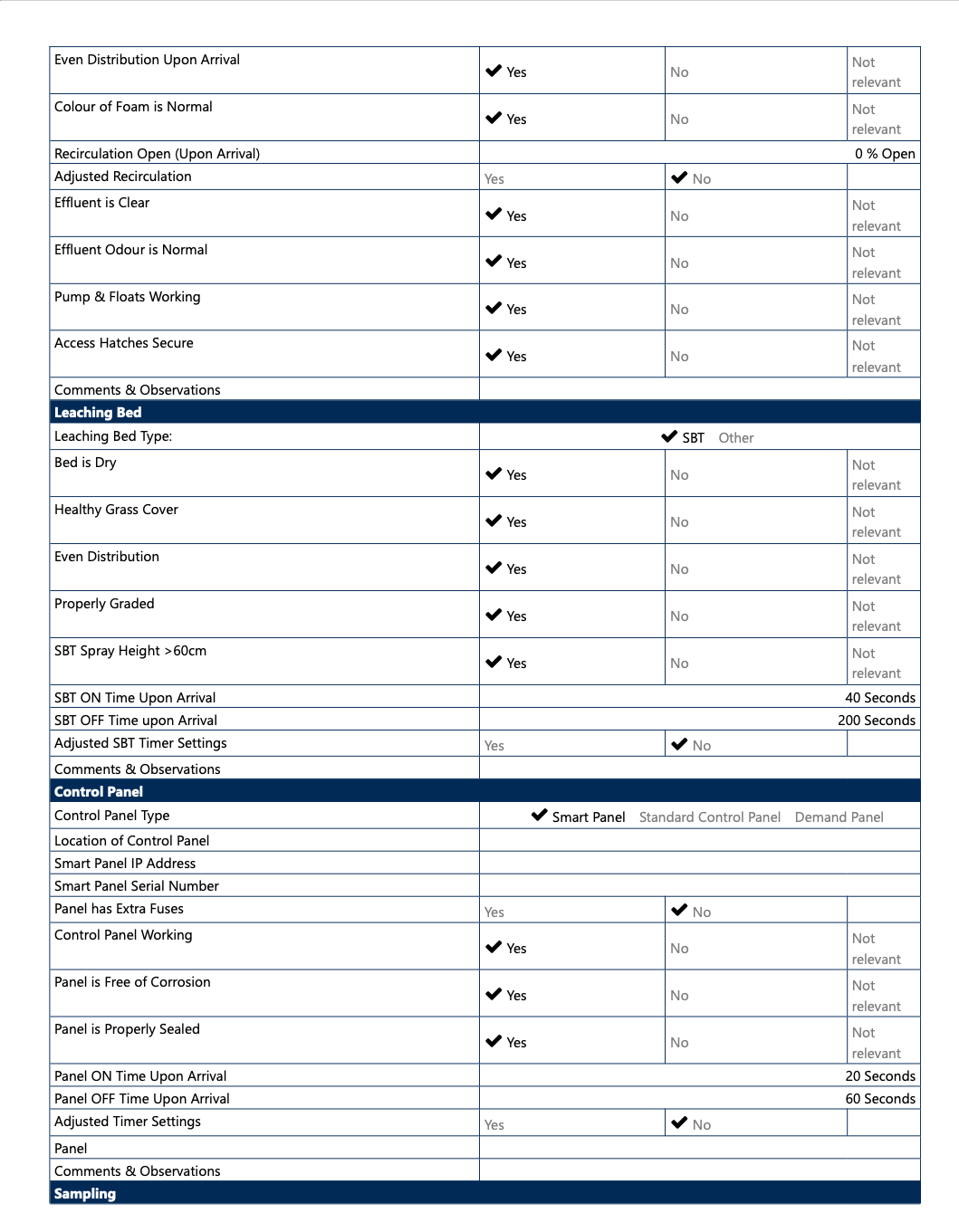
Even Distribution Upon Arrival
The technician will assess the spray distribution by examining the visual evidence of media saturation. The goal is to see that the spray pattern is even across the media and not concentrated in one area. The technician will look for irregular spray patterns and excess aersolization.
Colour Of Foam Is Normal
The technician looks at the colour across the treatment media. The colour of the foam media can indicate the maturity level of the bacteria, the effectiveness of the treatment up to that point, and the overall health of the system. The colour of the foam media is expected to darken over time, with use, and with the development of bacteria.
Adjusted Recirculation
The technician will check “yes” if they adjusted the valve. Recirculation does not apply to all systems and frequent adjustments are not necessary. New installs are advised to keep the valve closed for the first year to promote bacteria growth. During service visits, the technician can assess if it may be beneficial for treatment to open for improved treatment.
Effluent is Clear
This is a visual assessment of a sample collected effluent for an appearance of cloudiness or fog, or visible particulate matter; this helps us determine the effectiveness of the treatment and if system adjustments may be beneficial.
Effluent Oder is Normal
Technicians are familiar with “normal” or “off” smelling effluent. The odour can indicate the health of the system and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Pumps & Floats Working
The technician will test the floats by manually raising them to ensure they are engaging and sending a signal to the panel to trigger the pump. The technician will look for evidence the pump is engaging such as seeing the water move and hear the pump turn on and off. The technician will also test the amps that the pump is drawing if access to the panel is available.
Pumps & Floats Working
The technician will test the floats by manually raising them to ensure they are engaging and sending a signal to the panel to trigger the pump or timer. The technician will look for evidence the pump or timer is engaging. The technician will also test the amps that the pump is drawing as it works.
Waterloo Type Comments & Observations
This is where the technician will add commentary to the points above and notes any action or work completed.
Leaching Bed Section
The leaching bed is how the final effluent is dispersed.
Leaching Bed Type
Leaching Bed Type:
SBT: SBT stands for shallow buried trench which is a type of pressurized leaching bed. They are commonly U-shaped trenches which create a hollow spot under the surface with a 1 inch pipe runs through the middle of the hollow. The green lid at the end of the trench is where technicians access the trenches for maintenance.
Other: Other generally refers to a standard septic bed where 3 inch pipes sit on a bed of gravel and sand.
Bed Is Dry
Technicians will assess the leaching bed by walking across the it to identify any potential areas of concern. Areas of concern include areas that are overly saturated or swampy, or if there is evidence of ponding or pooling.
Healthy Grass Cover
Grass and other vegetative cover helps promote natural evaporation.
Even Bed Distribution
The technician will observe if the leaching bed is level and will look for marked variations in the turf or alternate ground cover such as pine bark.
Properly Graded
Proper grading helps prevent standing water in the leaching bed area. Poor grading may cause uneven distribution, pooling or alarms due to water flowing back to the system. The technician may also comment on other grading around the property if it will pose concern for the system, such as landscaping that directs rain water towards the system rather than shedding it away.
SBT Spray Height > 60cm
The technician will perform a “squirt test” and record whether the spray height meets a height of 60cm or more.
SBT Spray Height > 60cm
The technician will perform a “squirt test” and record whether the spray height meets a height of 60cm or more.
Leaching Bed Comments & Observations
Repairs to the leaching bed cannot be completed by Waterloo Biofilter technicians. This is where the technician will add commentary to the points above and make recommendations such as:
- Some areas of concern, there appears to be an animal nest or tunnels being created, homeowner should investigate to prevent any damage to the plumbing by animals.
- Some dry and dead patches of grass, homeowner should keep an eye on them and investigate if they get worse.
Control Panel Section
The control panel is how your system is controlled and where settings can be changed.
Control Panel Type
Control Panel Types:
Smart Panel: A Smart Panel is easily identifiable as having an interactive display screen and Waterloo Biofilter Systems Inc.’s distinctive blue, gray and white colour theme and logo. The interactive display screen is useful for showing error codes to aid effective trouble shooting and when customers have a remote monitoring service contract, a smart panel allows for a technician to log into the panel remotely to troubleshoot alarms, change settings, or retrieve data needed to resolve the alarm on site.
Standard Control Panel:
A standard panel is a simple gray or brown coloured heavy plastic panel box with breakers, toggle switches, and a timer (if applicable).
Location of the Panel
The technician will record where the panel is located in proximity to the system and may note accessibility features or limitations.
Control Panel IP Address
The IP address is the is how we connect to the system for readings.
Control Panel is Not Working
The technician tests if the panel has power going to it and is receiving signals from floats and able to send signals to the pumps. The technician may use an “amp clamp” or a “current clamp,” also known as a multimeter, to measure the amps being drawn which is an indication of the resistance the pump is encountering.
Control Panel is Free From Corrosion
Corrosion can be caused by moisture or gases getting into the panel. Corrosion is an indication that repairs are likely necessary; excessive corrosion can negatively impact the systems ability to function properly and will require the panel be replaced.
Control Panel is Properly Sealed
Each panel has a weatherproof gasket attached to the door which helps prevent water from penetrating from the exterior (such as rain). The technician will look for gaps or cracks where insects or water may penetrate the housing box. The technician will also examine the electrical conduit opening to ensure it is properly sealed to prevent gas from the system entering the panel.
Panel ON Time Upon Arrival
The technician will record the duration of time the pump is set to run for when it is triggered.
Panel OFF Time Upon Arrival
The technician will record the duration of time that the pump rests between actively pumping between chambers.
Adjusted Timer Settings
The technician will mark “yes” if they adjusted the settings and either record the changed settings in the comments or may take photos of the new setting. Timer settings can be changed to assist with treatment as well as in response to your specific use of the system.
Panel
The technician will attach multiple photos of the panel itself for reference.
Control Panel Comments & Observations
This is where the technician will add commentary to the points above and notes any action or work completed such as:
- Some evidence of moisture entering the panel; I dried any visible wet spots and looked for the source but there was no evident penetration site.
- Septic 8.2 amps and operating within normal parameters, disposal 9.1 amps and operating within normal parameters.
- Pumps run on demand.
- Added putty to fill gaps in the electrical conduit opening.
Page Two Definitions
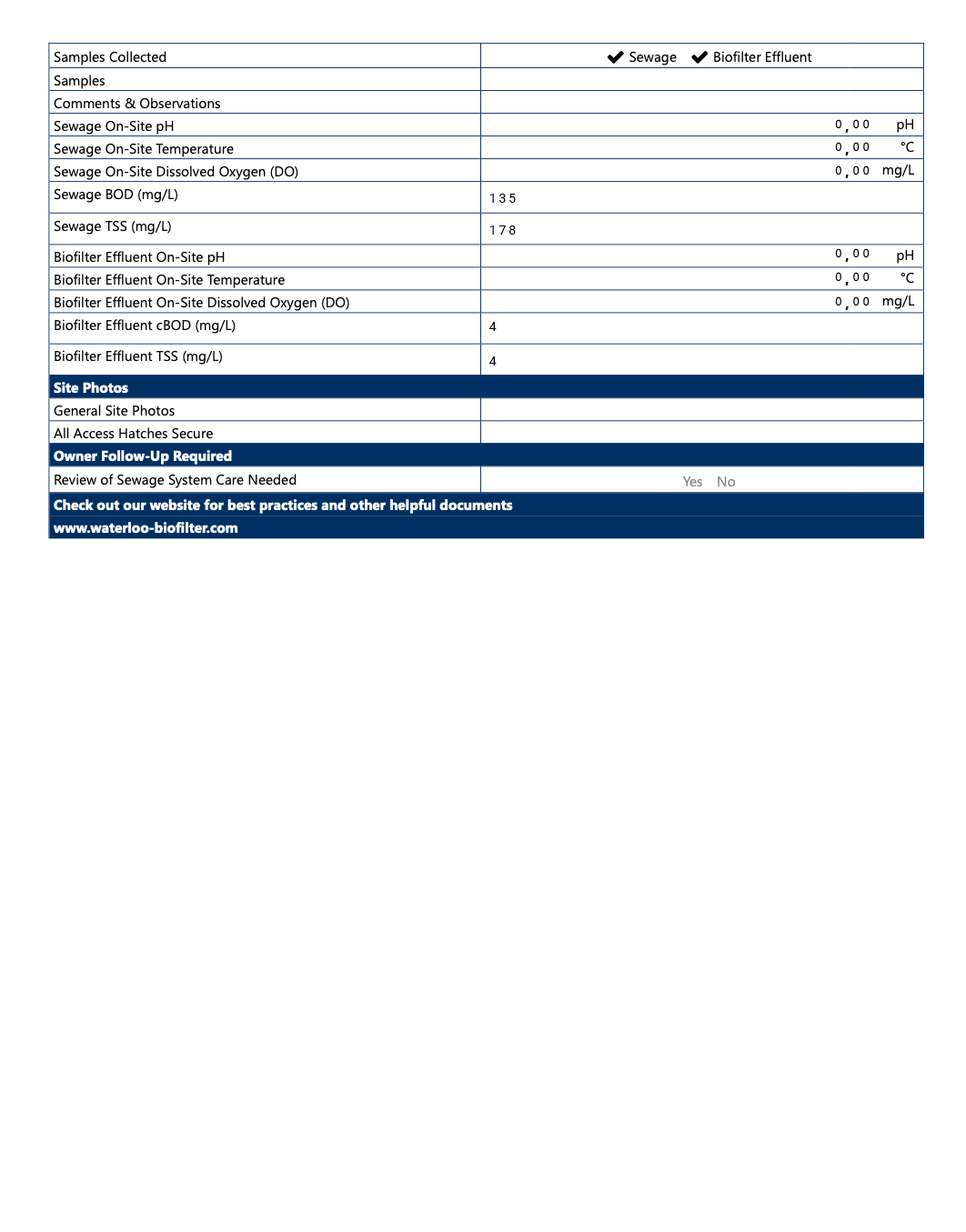
Samples
The technician will commonly add a photo of samples collected in a side-by-side view.
Samples Comments & Observations
This is where the technician will add commentary or notes specific to the samples collected. Sample appearance (colour, cloudy, suspended solids) will vary site to site as no two Biofilter sites are the same. Each Biofilter site is comprised of a unique bacterial environment and appearances can be deceiving. The appearance or odour of a sample is not determinative of whether treatment is successful or not, the organic analysis is what determines successful treatment.
Sewage On-site PH
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of pH testing which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab.
Sewage On-site PH
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of pH testing which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab.
Typical range may be 6-9.5
Sewage On-site Temperature
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of temperature readings which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab.
Typical range may be 4-35
Sewage On-site Temperature
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of temperature readings which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab.
Sewage On-site Dissolve Oxygen (DO)
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of dissolved oxygen levels which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab.
Typical range may be <1
Sewage BOD (mg/L)
This is a measurement of the dissolved oxygen needed by the aerobic biological organisms to break down organic matters. This value is provided by a third-party laboratory who tests the samples collected by the technician. Typical range may be 110-190
Sewage TSS (mg/L)
This is a measure of the dry-weight of suspended particles or non-dissolved particles present in the sewage sample. This value is provided by a third-party laboratory who tests the samples collected by the technician. Typical range may be 120-210
Biofilter Effluent On-Site PH
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of pH testing which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab. Typical range may be 6-9.5
Biofilter Effluent On-Site Temperature
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of pH testing which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab. Typical range may be 4-35
Biofilter On-site Dissolve Oxygen (DO)
Where possible, the technician will record in-situ results of temperature readings which provides additional data for comparison to results provided by the lab. Typical range may be >1
Biofilter BOD (mg/L)
This is a measurement of the dissolved oxygen needed by the aerobic biological organisms to break down organic carbon and nitrogen matters. This value is provided by a third-party laboratory who tests the samples collected by the technician.
Typical range may be 1-20
Biofilter TSS (mg/L)
This is a measure of the dry-weight of suspended particles (non-dissolved particles) present in the treated effluent sample. This value is provided by a third-party laboratory who tests the samples collected by the technician.
Typical range may be 1-20
Site Photos Section
Photos Taken By The Technician
General Site Photos
The technician will save photos of the site as it looks that day as a reference tool for both the technician and the Owner. The technician may include photos of anything that was of concern that they commented on to provide a visual reference so the Owner can see what the technician sees. Photos may also include before and after comparisons of filters or nozzles they cleaned, spray patterns on the foam media, or other reference points that they feel could be useful.
Owner Follow-up Required Section
This section denotes additional requirements for the system owner to follow up on.
Review of Sewage Care System
If the “yes” is checked, the owner should refer back to the best practices for optimal performance posted on our website. The technician may also comment regarding options for repairs that are recommended, or reiterate areas of concern that the Owner should follow-up on.